The kidneys have an important role in maintaining health. When the person is healthy, the kidneys maintain the body's internal equilibrium of water and minerals (sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sulfate). The acidic metabolism end-products that the body cannot get rid of via respiration are also excreted through the kidneys. The kidneys also function as a part of the endocrine system, producing erythropoietin and renin. Erythropoietin is involved in the production of red blood cells plays a role in bone formation.
In medicine, Dialysis is the process of removing excess water, solutes and toxins from the blood in those whose native kidneys have lost the ability to perform these functions in a natural way. This process helps keep your fluids and electrolytes in balance when kidneys are unable to function properly.
This is referred to as renal replacement therapy. Dialysis may be used in those with rapidly developing loss of kidney function, called acute kidney injury (previously called acute renal failure); or slowly worsening kidney function, called Stage 5 chronic kidney disease, (previously called chronic kidney failure and end-stage renal disease and end-stage kidney disease).
Dialysis is used as a temporary measure in either acute kidney injury or in those awaiting kidney transplant and as a permanent measure in those for whom a transplant is not indicated or not possible. Dialysis is a treatment that filters and purifies the blood. Dialysis has been used since the 1940s to treat people with kidney problems. The two main types of dialysis, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, remove wastes and excess water from the blood in different ways.
In hemodialysis, the patient's blood is pumped through the blood compartment of a dialyzer, exposing it to a partially permeable membrane. Hemodialysis removes wastes and water by circulating blood outside the body through an external filter, called a dialyzer, that contains a semipermeable membrane. The blood flows in one direction and the dialysate flows in the opposite.
In peritoneal dialysis, a sterile solution containing glucose (called dialysate) is run through a tube into the peritoneal cavity, the abdominal body cavity around the intestine, where the peritoneal membrane acts as a partially permeable membrane.
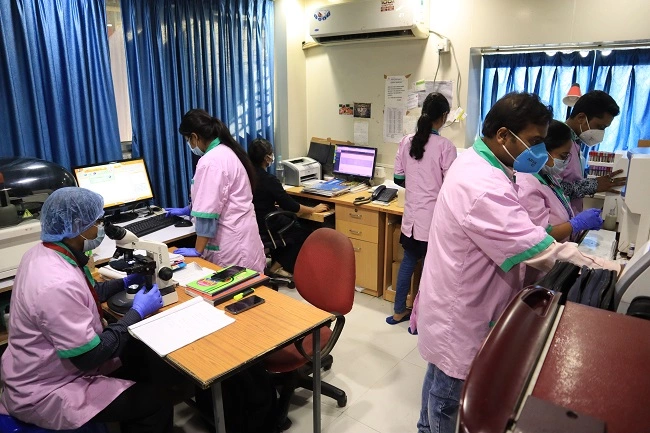
Our Free Dialysis units play a great role in in helping the dialysis patients to lead a normal life. At Eskag Sanjeevani we provide Dialysis treatment in a cheerful ambience and by positive minded staff in proper sterile techniques leading to better outcomes.
At Eskag Sanjeevani, our free Dialysis centre with the following state-of-the-art facilities, free of cost.
I am really pleased about hospital services like billing, security,and also maternity ward really good my wife enjoyed that atmosphere.
Generic
It is a very good Nursing home. All are well behaved & helpfull.Specially Nursing staff are well trained, laborious, talking like family member. Doctors are also. Food Quality is very good & tasty.
Generic
My experience of treatment is wonderful...highly recommended for cost effective treatment
Generic
Very good hospital
Generic
Awesome environment in this hospital... My experience was vary good... I recommended to everyone...
Generic
Low cost treatment given by professional and kind staffs....I would highly recommend this hospital,
Generic
Excellent ambiance...very good behaviour of hospital staffs...cost effective treatment is provided.
Generic
Very Good atmosphere and very satisfied treatment for every patient. Thanks and regards
Generic
Very good treatment,very good pharmacy system, outstanding behaviour of all staffs. I am satisfied.
Generic
Hospitality of this nursing home is excellent... I had my c section under dr Mala Basu here in 2009.. N I felt like home... N kudos to the staff working... One stop for medical guidance
Generic